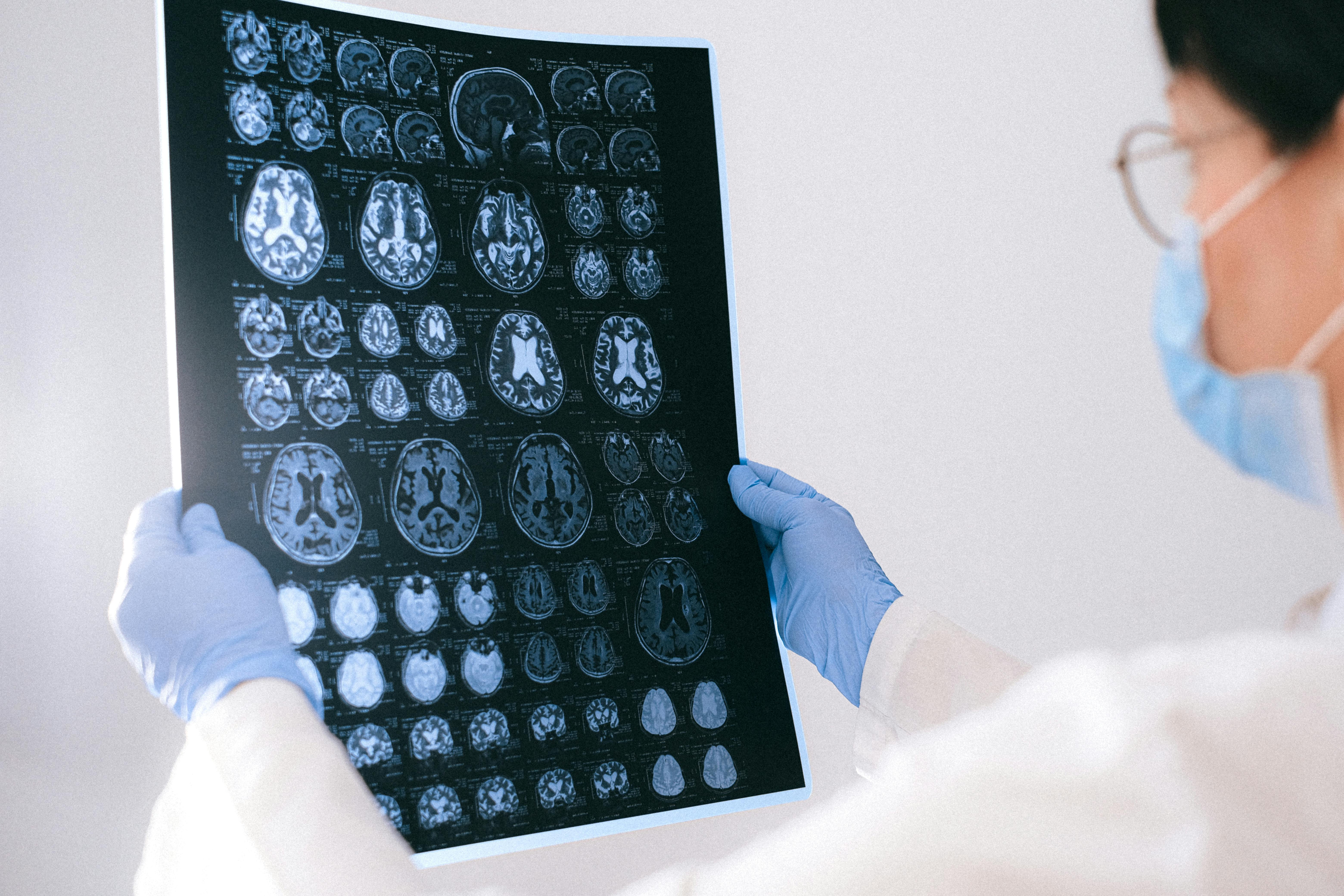
A mini stroke is also called a Transient Ischaemic Attack or TIA. It is a brief episode of dysfunction in the brain. Like a stroke, TIA’s onset is sudden, over a few seconds or minutes.
People having a mini stroke can experience a variety of symptoms. The most important are weakness on one side affecting the face, arm or leg – or all three – or speech disturbance, which can be slurring or decreased speech fluency or comprehension. These are the typical symptoms, but sometimes people can experience visual loss, dizziness or vertigo.
Patients having a mini stroke return to normal within minutes or hours after the event. This gives the false impression it may not be serious and patients do not always seek medical attention. But it is very important if you or someone in your family experiences any of the above symptoms, they immediately visit their nearest emergency department.
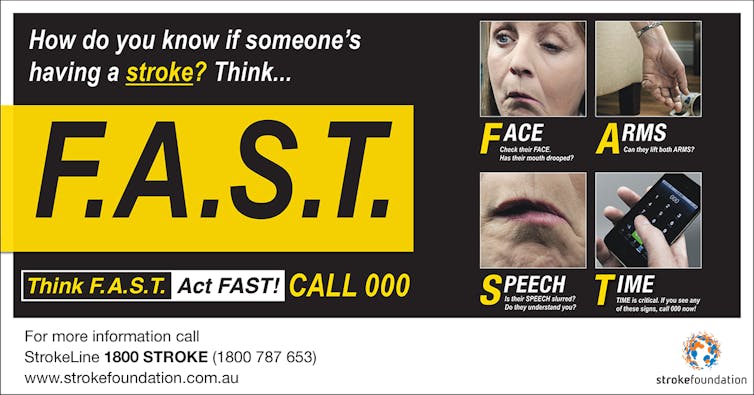 |
If you believe you or someone in your family is having a
mini stroke, you should immediately visit the nearest emergency
department. The
Stroke Foundation |
Why a Mini Stroke Is Serious
In a mini stroke, there is an interruption to the brain’s blood supply. As a consequence, some brain cells receive less oxygen and nutrients than they need. The period of poor blood flow can last from a few minutes to 24 hours. The longer it lasts, the more risk there is of brain cells dying.
Blood supply restriction to any body tissues is called ischaemia; an area of the brain where the cells are deprived of blood supply is called an ischaemic area. If the cells die this is called a stroke, or ischaemic attack, as opposed to a transient ischaemic attack. In a transient ischaemic attack though, brain function is impaired which causes symptoms, but the cells survive.
Anyone can have a mini stroke but it is more frequent in patients who have risk factors for blood vessel damage: old age, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking and raised cholesterol levels.
Heart conditions leading to an irregular and fast heart rate, called atrial fibrillation, and disorders that mean blood has a tendency to form clots, are also causes of mini strokes. These are the same factors that can lead to a stroke.
A mini stroke is a strong warning of something more serious, like a stroke. Patients who have had a mini stroke are 10% more likely to have a stroke over the following four weeks. More than 40% of these happen in the first 48 hours.
Once a stroke does occur, treatment outcomes are much poorer. A large stroke in which a substantial volume of brain dies can be fatal, or produce a lifetime of disability. Potentially serious and disabling strokes can be prevented if a mini stroke is recognised. Adequate investigation and treatment will reduce the risk of a disabling stroke.
How to Reduce Risk of Stroke
If a person has a mini stroke and is assessed in an emergency department, doctors will investigate to understand the cause of the event. Initial tests will include measuring a patient’s blood pressure and doing blood tests to exclude high cholesterol and diabetes.
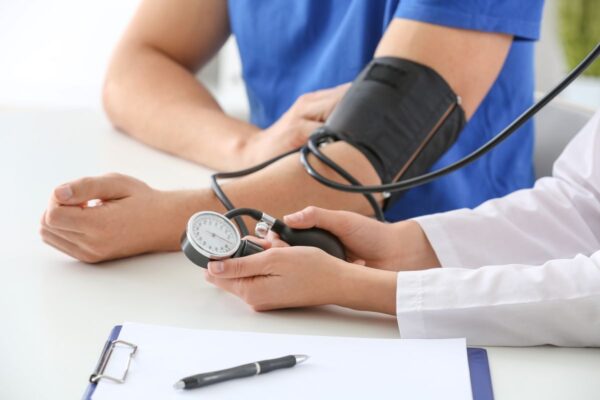 |
At the hospital, initial tests will include checking the
patient’s blood pressure. (Shutterstock) |
A CT scan or MRI will be done, to provide a picture the brain. In a mini stroke, this should be normal, as the brain cells have survived. The brain scan is also done to exclude another diagnosis such as a brain tumour, which can also be the cause of the symptoms.
The doctor will also examine the neck arteries, with either a CT or an ultrasound, for a narrowing or blockage causing decreased blood supply to the brain. If there is a blockage, the doctor will decide whether this requires an operation.
She will check the patient’s heart to exclude a condition leading to clot formation. Factors that can cause clots to form in the heart include enlarged heart chambers, malfunction of the heart valves and an irregular heart rate.
The treatment of a mini stroke will include three different medications: a medicine to reduce the risk of blood clots, such as aspirin; a medication to decrease blood pressure, such as perindopril; and a cholesterol lowering drug, such as atorvastatin.
Almost all patients who have had a mini stroke should be on these three medications. Even with normal cholesterol or normal blood pressure, research shows these medications reduce risk of subsequent stroke. Other treatments may include help stopping smoking, diabetes treatment and advice about diet, exercise and weight loss.
The important message is; if you have sudden onset of weakness or speech disturbance seek urgent medical attention even if the symptoms improve quickly.
Important Notice: This article was originally published at www.theepochtimes.com by Candice Delcourt where all credits are due.
Disclaimer
The watching, interacting, and participation of any kind with anything on this page does not constitute or initiate a doctor-patient relationship with Veripeudic.com or Life Preserver. None of the statements here have been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of Veripeudic.com or Life Preserver are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The information being provided should only be considered for education and entertainment purposes only. If you feel that anything you see or hear may be of value to you on this page or on any other medium of any kind associated with, showing, or quoting anything relating to Veripeudic.com or Life Preserver in any way at any time, you are encouraged to and agree to consult with a licensed healthcare professional in your area to discuss it. If you feel that you’re having a healthcare emergency, seek medical attention immediately. The views expressed here are simply either the views and opinions of Veripeudic.com or Life Preserver or others appearing and are protected under the first amendment.
Veripeudic.com or Life Preserver promotes evidence-based natural approaches to health, which means integrating her individual scientific and clinical expertise with the best available external clinical evidence from systematic research. By individual clinical expertise, I refer to the proficiency and judgment that individual clinicians acquire through clinical experience and clinical practice.
Veripeudic.com or Life Preserver does not make any representation or warranties with respect to the accuracy, applicability, fitness, or completeness of any multimedia content provided. Veripeudic.com or Life Preserver does not warrant the performance, effectiveness, or applicability of any sites listed, linked, or referenced to, in, or by any multimedia content.
To be clear, the multimedia content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health providers with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read or seen in any website, video, image, or media of any kind. Veripeudic.com or Life Preserver hereby disclaims any and all liability to any party for any direct, indirect, implied, punitive, special, incidental, or other consequential damages arising directly or indirectly from any use of the content, which is provided as is, and without warranties.

